Fruit:-
- The ovary develops into a fruit. The transformation of ovules into seeds and ovaries into fruit proceeds simultaneously.
- The wall of the ovary develops into the pericarp (wall of the fruit).
- The fruits may be fleshy (e.g. guava, orange, mango, etc.) or may be dry (e.g. groundnut, mustard, etc).
- Many fruits have mechanisms for dispersal of seeds.
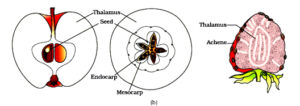
- Fruits are 2 types:
- 1. True fruits: In most plants, the fruit develops only from the ovary, and other floral parts degenerate and fall off. They called true fruits.
- 2. False fruits: In this, the thalamus also contributes to fruit formation. E.g. apple, strawberry, cashew, etc.
- In some species, fruits develop without fertilisation. Such fruits are called parthenocarpic fruits. E.g. Banana.
- Parthenocarpy can be induced through the application of growth hormones, and such fruits are seedless.